Describe the Structure and Function of Lysosomes
20 What cell is a real powerhouse. Lysosomes are acidic membrane-bound organelles found within cells usually around 1 micrometre in length.

Parts Of A Human Cell Diagram Of The Human Cell Illustrating The Different Parts Of The Cell Human Cell Diagram Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure
A lysosome is a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that many eukaryotic cells use to digest macromolecules.

. They are spheres made up of a lipid bilayer that encloses fluid that contains a variety of hydrolytic enzymes. 21 What are the two main functions of lysosomes. The enzymes present within lysosomes are also called as acid hydrolases as they work best at.
Answer 1 of 4. Lipids lipases carbohydrates glycosidases proteins proteases. 18 Which organelle is considered the substitute of lysosome in plant cells Why.
Lysosome are tiny vesicles filled with digestive enzymes. Lysosomes contain numerous hydrolytic enzymes which catalyse hydrolysis reactions. Phagocytosis is the engulfment of smaller organisms or food particles by a cell cell eating while autophagy is the recycling of the cells own organic material self eating.
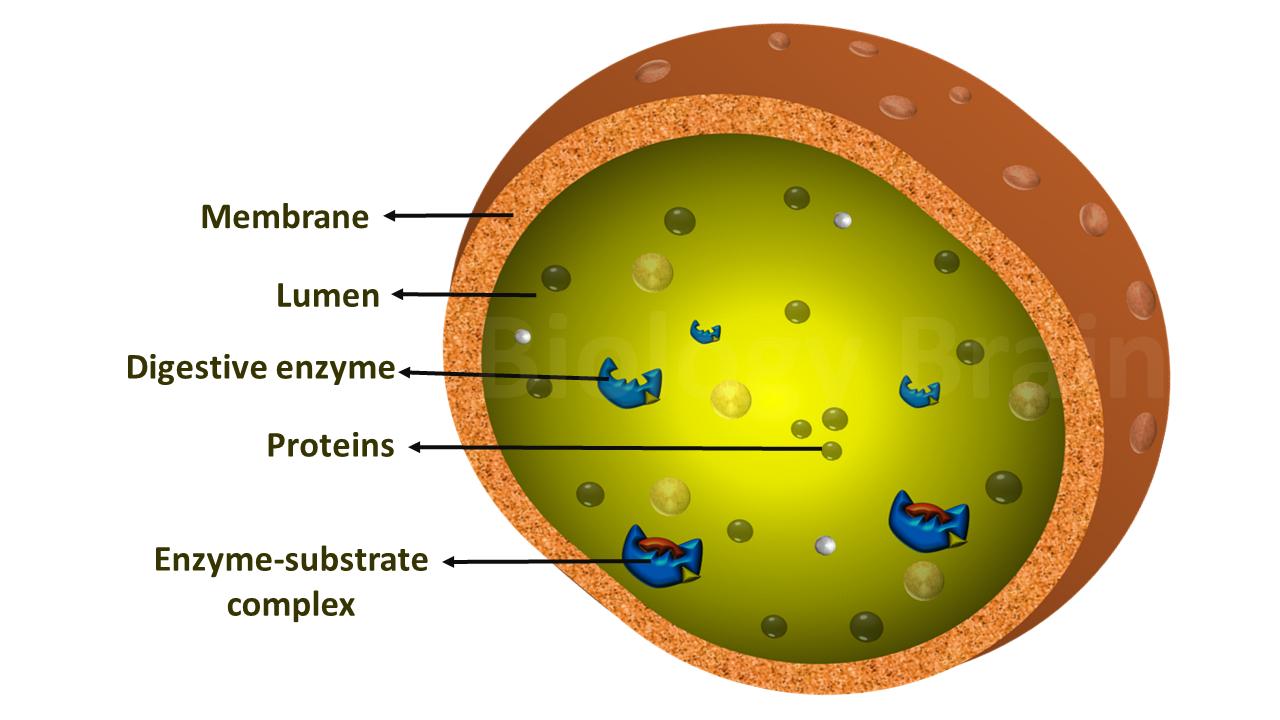
Lysosomes digest the organic waste that is produced due to the various metabolic activities of the cell. The lysosome size ranges between 01 to 12μm. - Each lysosome is surrounded by a single membrane - Lysosomal interior is acidic pH 4-5 - Lysosomes contain over 40 hydrolytic enzymes capable of degrading.
Remove organelles that no longer function. 16 What are lysosomes describe their functions. A lysosome is an organelle containing digestive enzymes which it uses to function as the digestion and waste removal for cells food particles bacteria etc.
These are found on the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum and are sites for protein synthesis of the cell. Digestion of intracellular or extracellular material nutrition from digested macromolecules and defenceprotection from harmful substances. -Responsible for digestion endocytosed material.
The function of lysosomes is to remove waste as well as destroying a cell after it has died called autolysis. -Range in size from 25nm to 1 um in diameter. Lysosome Structure Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles and the area within the membrane is called the lumen which contains the hydrolytic enzymes and other cellular debris.
Peroxisomes vary in shape size and number depending upon the energy requirements of the cell. - Explain the structure of cilia and flagella and the mechanism of their movement. The enzymes involved in lipid metabolism are synthesised on free ribosomes and selectively imported to peroxisomes.
For a lysosome its functions include. Lysosomes are simple tiny spherical sac-like structures evenly distributed in the cytoplasm Each lysosome is a small vesicle surrounded by a single membrane and contains powerful enzymes. Digestive enzymes help speed up breaking things down chemically.
These are small round sacs that contains digestive enzymes which break down structures and substances. Structure of lysosomes. The studies of lysosome physiology described here are basic in nature but.
They play an important function is removing the worn out cell organelles and organic debris by a process called. A complex semi-rigid structure responsible for the shape of the cell. These are used to kill the bacteria or virus in WBC while in tadpole-tail cells they kill the cell by separation of the tail from the main body.
Pulse-chase cell fractionation procedures will. These are made of a phospholipid bilayer with many membrane-bound proteins. 19 Why do lysosomes have a single membrane.
Lysosomes are generally very small ranging in size from 01-05 µm though they can reach up to 12 µm. Lysosomes are only found in animal cells. -Contains acid hydolases active at pH45 -High internal proton concentration is maintained by a proton transporter H ATPase on the lysosomal membrane.
Describe the structure features and function of lysosomes. In other words lysosomes are membranous organelles whose specific function is to breakdown cellular wastes and debris by engulfing it with hydrolytic enzymes. Describe the structure and function of primary bronchus.
A human cell contains around 300 of them. The major function is to prevent bacterial cells from rupturing when the water. Describe the formation structure and functions of the lysosomes.
Will be valuable to our understanding of lysosome related pathologies at. They are also involved in the transport of materials in and out of the cell. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are vacuoles which contain digestive and destructive membranes.
Enzymes speed up a chemical reaction. Lysosomes are a cell organelle translating as an independent structure within a cell possessing a specific structure and function. Structure and function in normal cultured cells.
The function is to transport air to the rest of the body. Vesicles are small spheres of fluid surrounded by a lipid bilayer membrane and they have roles in transporting molecules within the cell. Is the function of lysosomes the same in all cells.
The membrane surrounding the lysosome is vital to ensure these enzymes do not leak out into the cytoplasm and damage the cell from within. 15 Is lysosome present in human body. Lysosomes small organelles filled with digestive enzymes.
They appear spherical and enveloped by single layer of phospholipids bilayer. These enzymes are capable of digesting or breaking down all organic materials. In animal cells they are usually spherical.
However their shape and size may vary to some extent in different organisms. Breakdown of lipids carbohydrates and proteins. Lysosomes are spherical bag-like structures that are bound by a single layer membrane.
They are found in all eukaryotic cells and act as garbage disposal or the digester of the cell. Compare and contrast the processes of phagocytosis and autophagy. 1The lysosome is the membrane bound organelle round in shape and surrounded by the single layer of the outer membraneThe lysosomes are filled with the acidic contents digestive enzymes which is involved in cellular processesThe single layered l.
Explain the following properties of water that make it the cradle of life. Lysosomes are specialized vesicles within cells that digest large molecules through the use of hydrolytic enzymes. They have a simple structure.
The lipids that make up the bilayer are phospholipids which are molecules. 17 Do lysosomes contain lysozyme. Describe the structure and function of a lysosome.
- Describe the structure of bacterial flagellum. Be used to study the turnover of cathepsin D as it relates to lysosome.
Describe The Structure And Function Of Lysosomes Lifeeasy Biology Questions And Answers

What Is Lysosome Function Definition Structure Importance

Lysosomes Structure Definition Function Diagram

Aas Study Lysosomes Science Cells Cells Project Cell Analogy

Cell Organelles Structure And Functions With Labeled Diagram Cell Organelles Organelles Human Cell Structure

A Brief Understanding Of The Major Functions Of Lysosomes Cells Project Cell Membrane Function

Lysosomes Holds Wastes And Has Enzymes To Break Down Waste And Hold Stuff Structure And Function Cell Structure Enzymes

Regulation Of The Life Cycle And Functions Of Lysosomes By Download Scientific Diagram
Lysosomes Structure Synthesis Function Teachmephysiology

Lysosome Structure Biology Wise

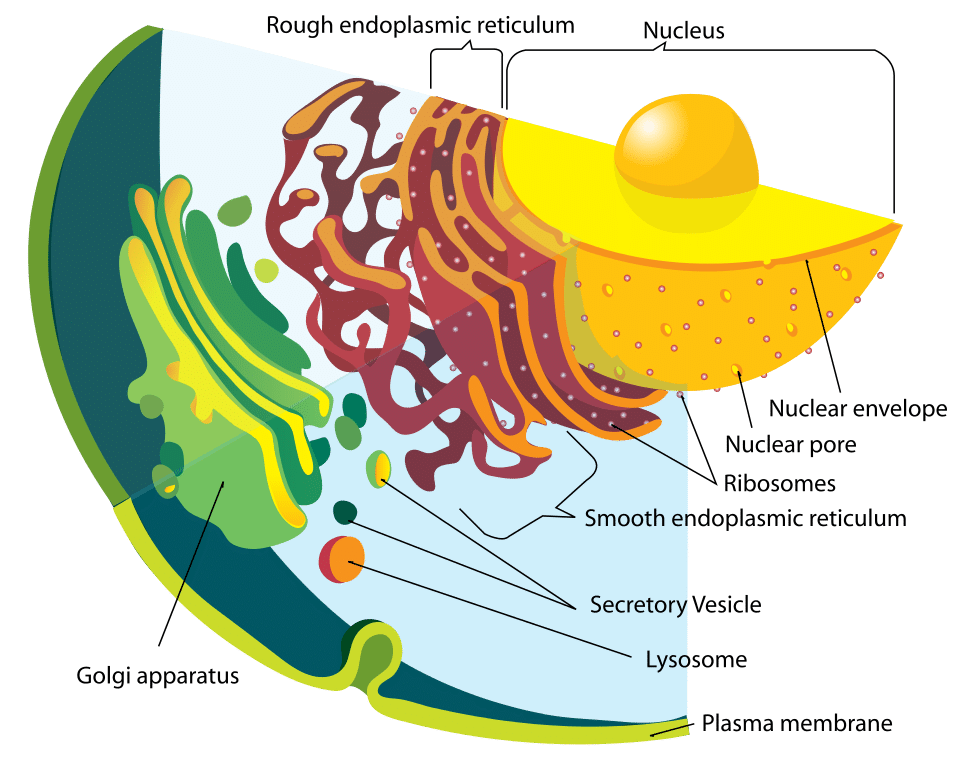
The Structure Of Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough And Smooth Er Diagram Cell Membrane Structure And Function Things Under A Microscope

Lysosome Structure Function Expii

Lysosome Structure And Function Youtube

Animal Vs Plant Cells Plant And Animal Cells Cell Organelles Plant Cell

Image Result For Cell Organelles And Their Functions Chart Cytoplasm Cell Organelles Organelles Cells Worksheet

Lysosomes Definition Structure Functions And Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment